2D Transformation in Computer Graphics
What is 2D Transformation?
- 2D transformation is like changing the position, size, or orientation of a 2D object on a computer.
- 2D transformation is like tweaking, adjusting, or changing the way a flat picture looks on a computer screen.
- 2D transformation is the backbone of manipulating graphics on a computer screen.
- It's like the toolkit for changing how 2D images appear.
Basic Geometrical Transformations:
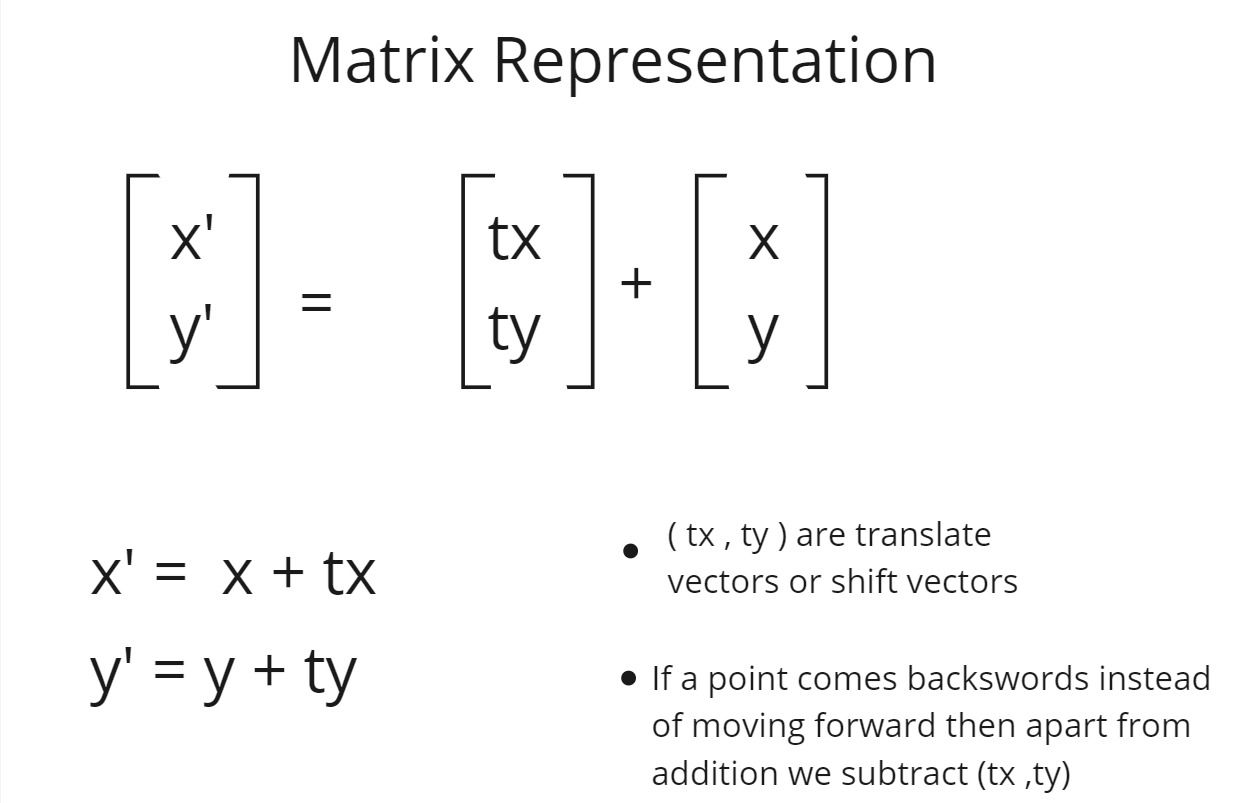
Matrix Representation of Translation
Translation
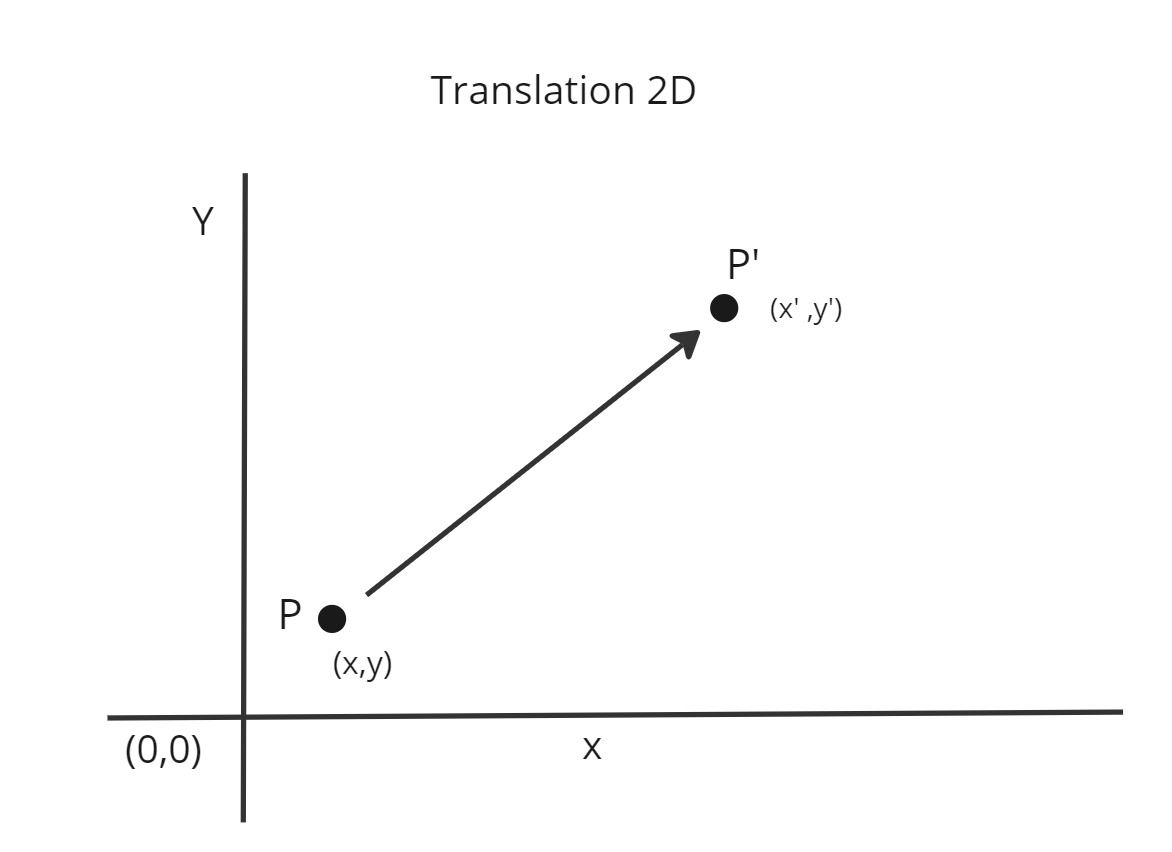
Translation in 2D transformation is like picking up an object on your computer screen and moving it to a new location.
- tx and ty are the translation vectors on x-axis and y-axis.
- tx represents the translation change on the x-axis.
- ty represents the change on the y-axis.
- A simple identity matrix will be used to represent the Translation Matrix.
- Translation simply represents that an object is being moved to another place
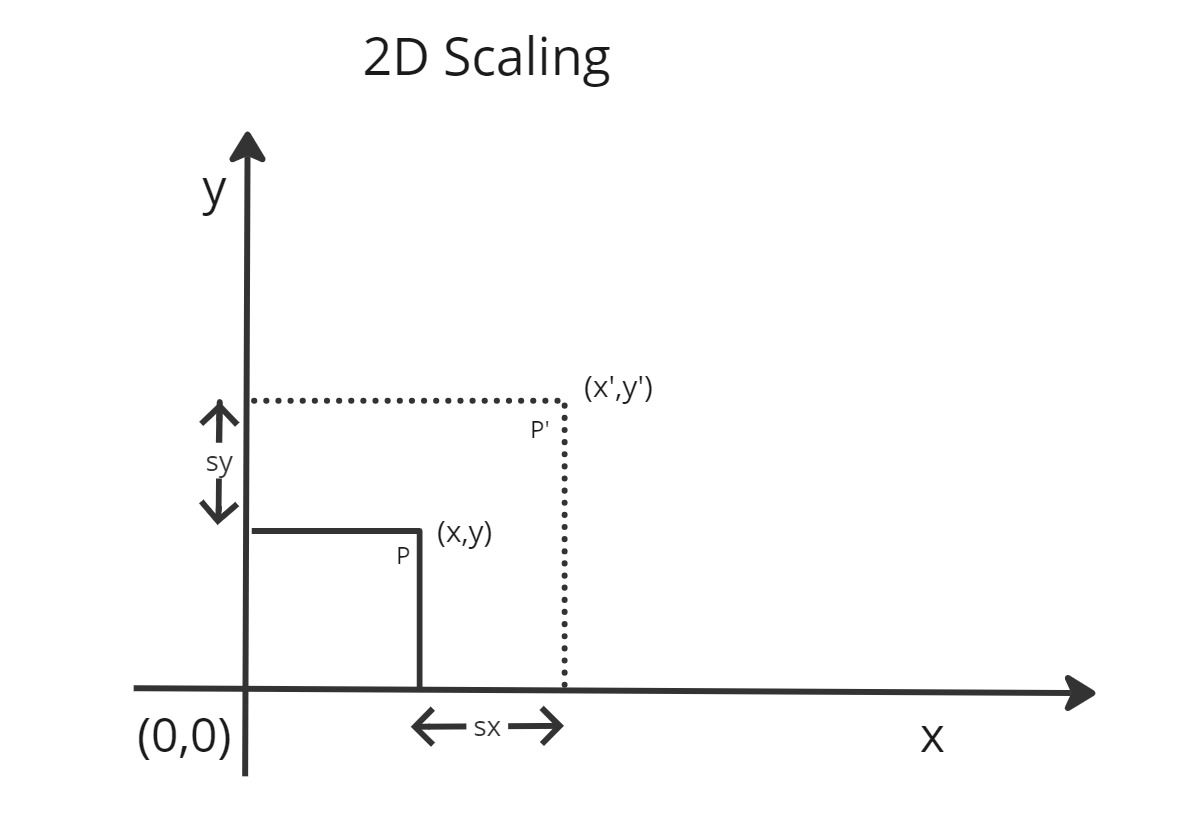
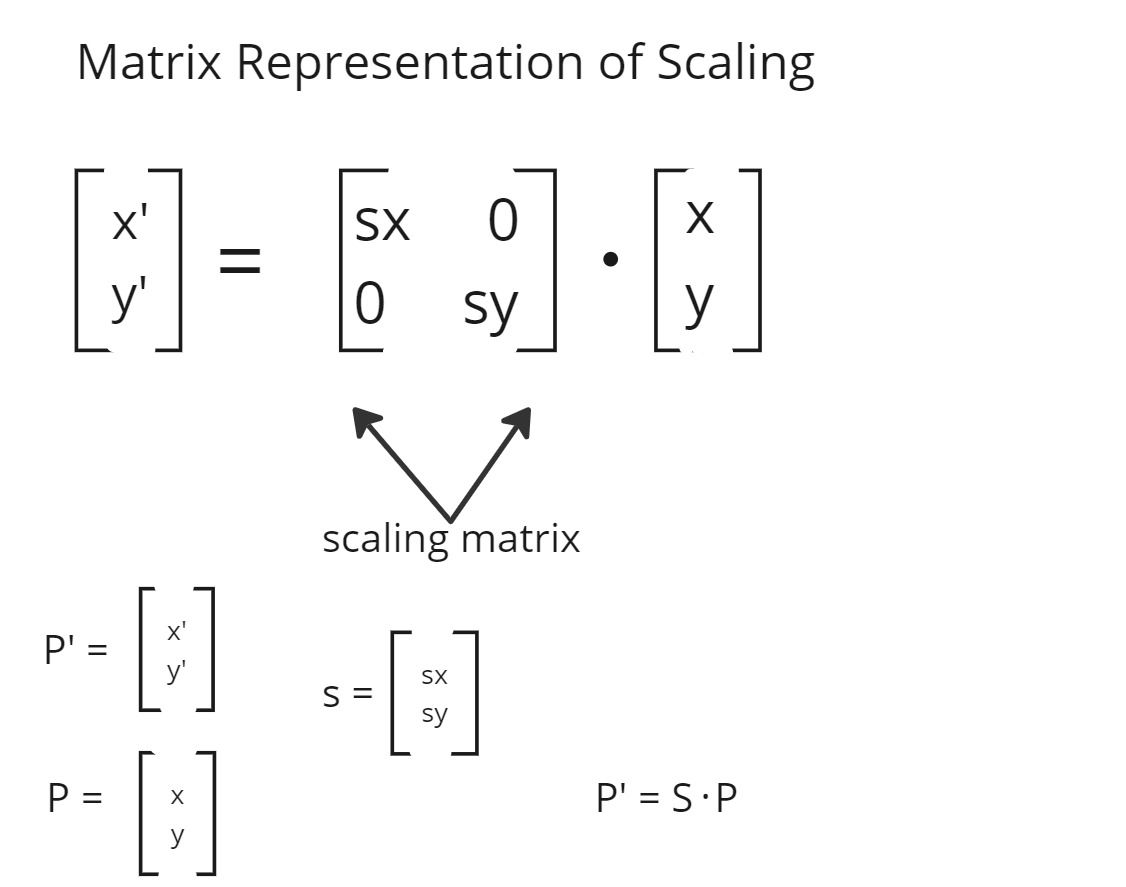
Matrix Representation of Scaling
What is Scaling in 2D transformation?
- Scaling in computer graphics is like changing the size of an object on your computer screen.
- Scaling is all about changing the size of objects on your computer screen.
- The matrix used in the representation of scaling is known as the scaling matrix.
- scaling coordinates are defined as sx and sy for the x-axis and y-axis.
- we can say that (x',y') is the product of (sx,sy) and (x,y)
Rotation
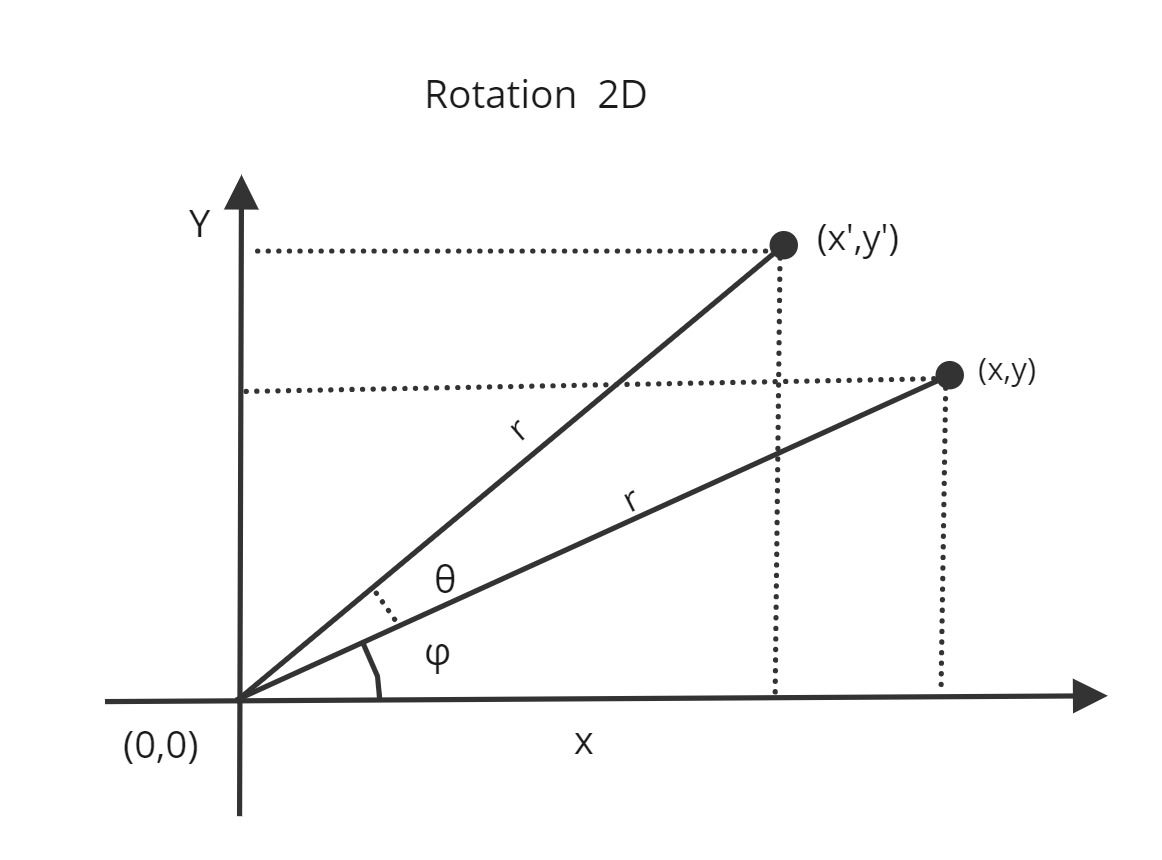
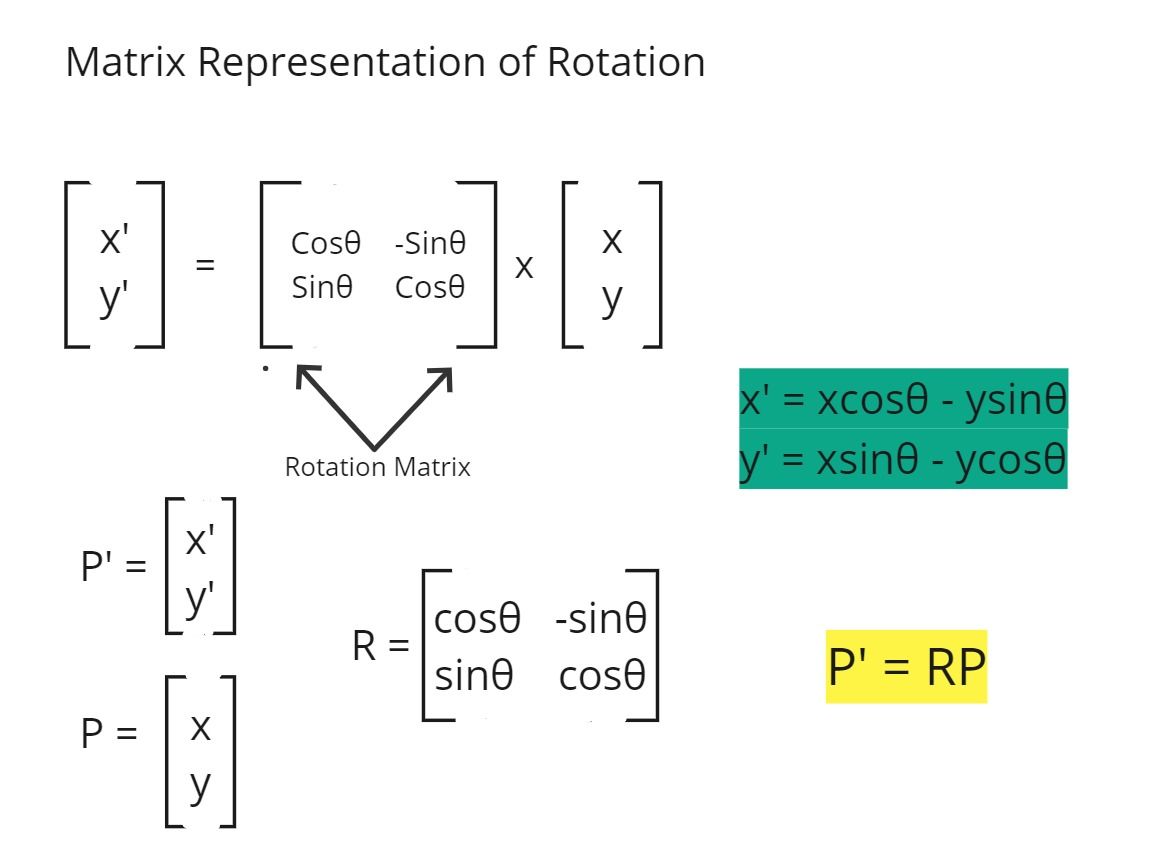
Matrix Representation of Rotation
- 2D rotation is a transformation that involves turning an object or image in a two-dimensional space around a specific point, known as the pivot point.
- Rotation in a 2D matrix involves turning the entire matrix around a chosen point, either clockwise or counterclockwise.
- Rotation in 2D is like turning an entire picture or grid around a specific point. You can rotate it either in the direction of a clock's hands (clockwise) or the opposite way (counterclockwise).
- The matrix used in the above figure is known as the Rotational Matrix
Derived Geometrical Transformation
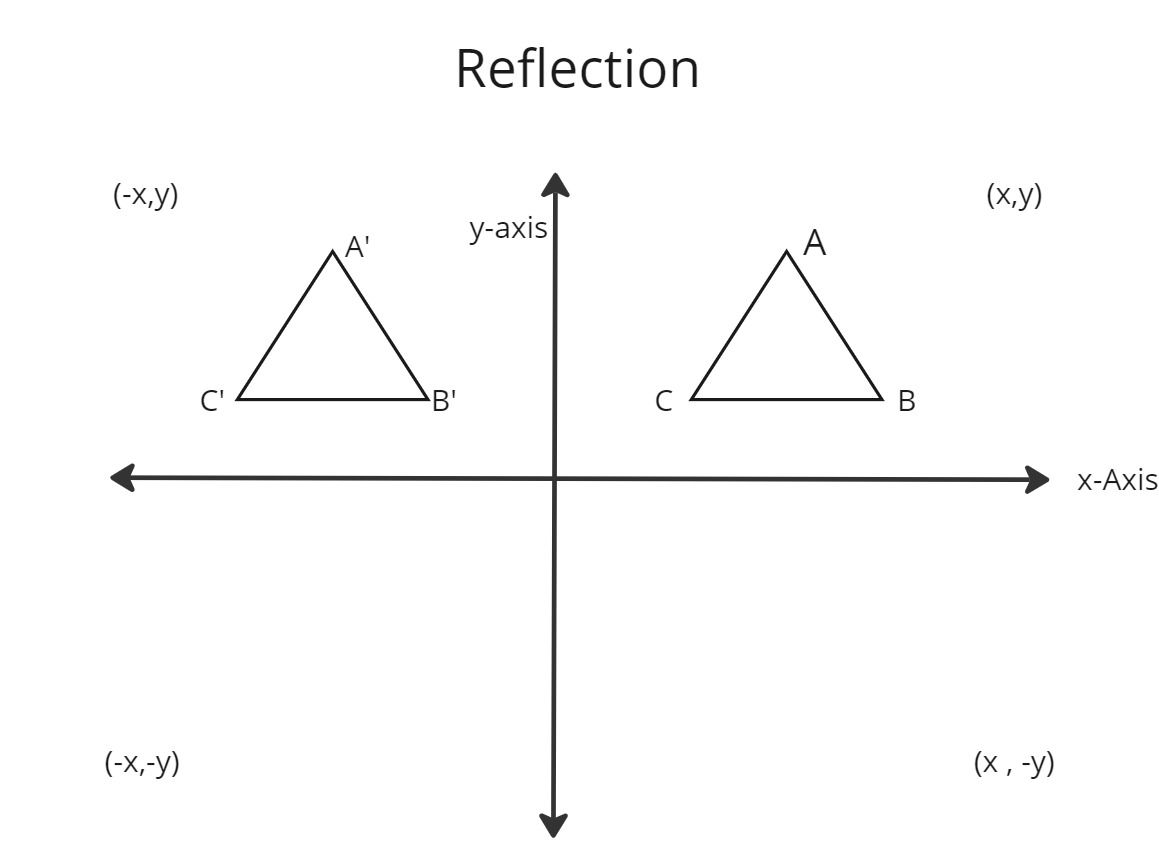
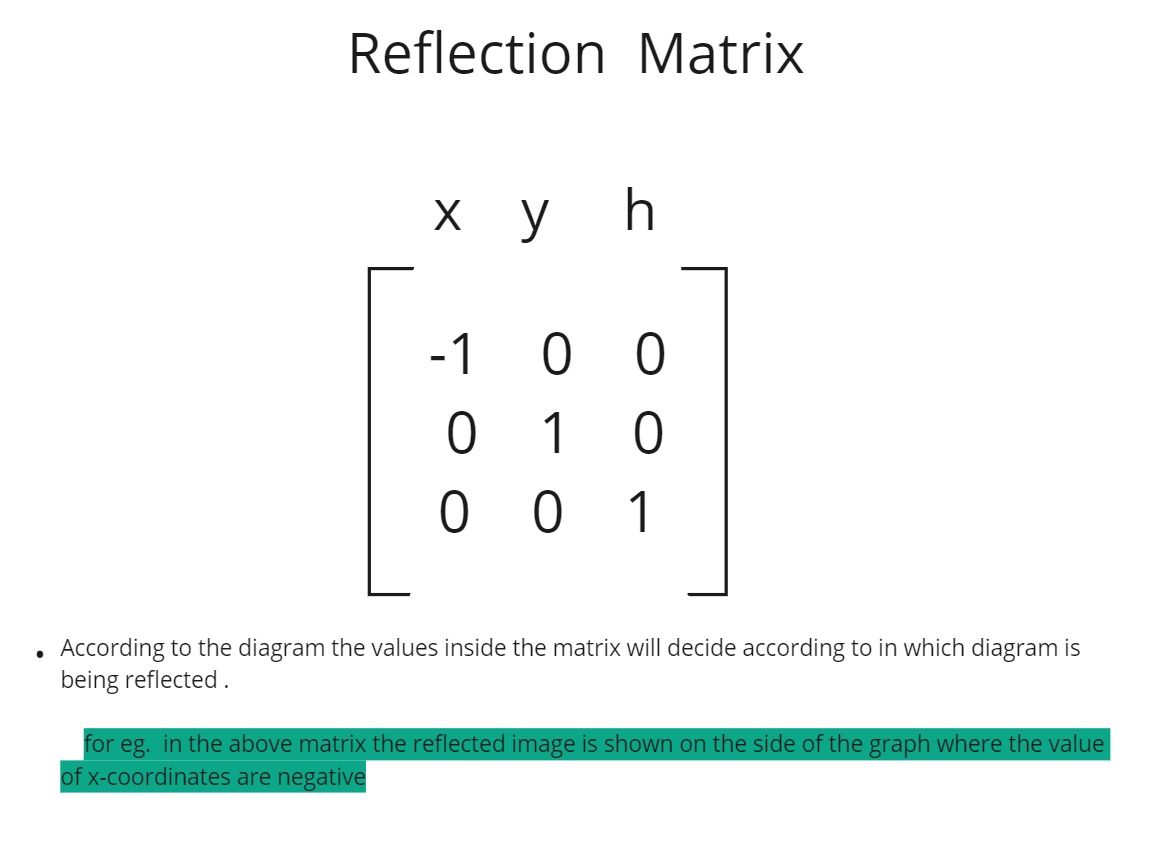
Reflection
- In 2D transformation, reflection is a process that involves flipping an object or image over a line and creating its mirror image.
- In 2D, the rotation is also described as the rotation transformation by θ = 180.
- Reflection about line X is accomplished with the transformation matrix . Reflection occurs around a specific line called the axis of reflection.
- The object is flipped across this line. Combining reflections is equivalent to a single reflection.
- For instance, reflecting twice about the x-axis is the same as no reflection.
- In computer graphics, reflection is used to create symmetrical images or simulate reflective surfaces.