
Survey , Static , Dynamic and Interior Routing Protocols
Routing Protocols
- Routing protocols are essential for ensuring efficient and reliable communication in IoT networks.
- These protocols define the rules and processes for how data is transmitted from one device to another across the network.
- Given the diverse and resource-constrained nature of IoT devices and applications,
- specialized routing protocols are developed to meet specific requirements such as energy efficiency, scalability and low latency.
Survey Routing Protocols
- Survey routing protocols refer to the comprehensive study and categorization of various routing protocols designed for IoT networks.
- This involves analyzing different protocols based on their characteristics and suitability for specific IoT applications.
- The aim is to provide a detailed overview and comparison of existing routing protocols to help researchers,
- developers and practitioners choose the most appropriate protocol for their IoT deployments.
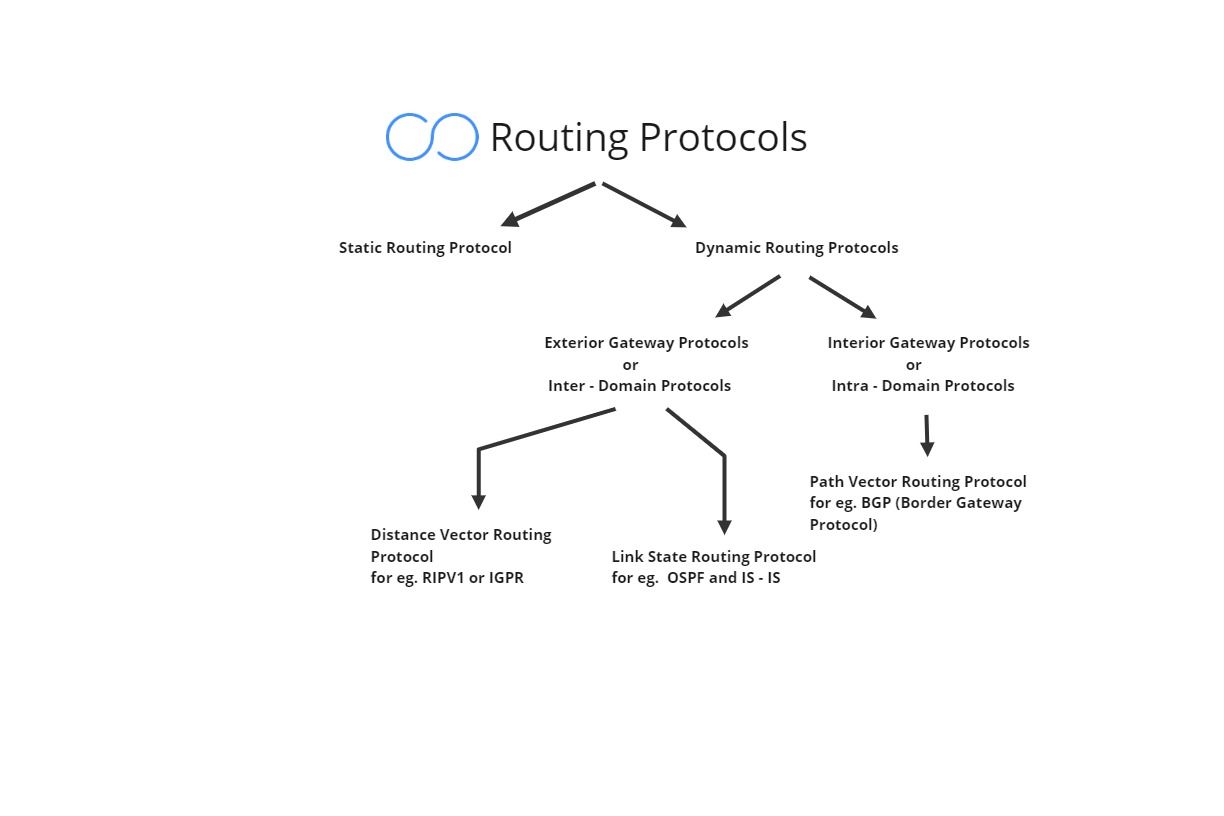
Static Routing Protocols
- Static routing involves manually configuring routes in network devices, such as routers or switches.
- static routing involves manually configuring routes, offering simplicity but limited adaptability.
- Dynamic routing protocols, on the other hand, enable automatic route
- discovery and adjustment to network changes, providing scalability and optimized routing in complex environments.
- The choice between static and dynamic routing depends on the network's size, complexity, and the level of adaptability and automation required.
Dynamic Routing Protocols
- Dynamic routing protocols are algorithms used by routers and switches to
- dynamically exchange routing information and automatically adjust to changes in network topology.
- dynamic routing protocols enable routers to discover network paths, determine the best routes, and adapt to network changes without manual intervention.
- Dynamic routing protocols play a crucial role in modern computer networks by providing automatic route discovery, adaptability and resilience.
- They enable routers to dynamically exchange routing information, calculate optimal routes, and adapt to changes in network conditions,
Interior Gateway Routing Protocols
- Interior Gateway Protocols (IGPs) are a category of dynamic routing protocols used within
- single autonomous system (AS), such as an organization's internal network.
- Interior Gateway Protocols (IGPs) are a vital component of dynamic routing protocols,
- enabling routers within the same autonomous system to exchange routing information and dynamically update their routing tables.
- IGPs play a critical role in optimizing routing decisions, discovering network
- topology, and ensuring efficient communication within the boundaries of a single administrative domain.
Distance Vector Routing
- A distance-vector routing protocol is a type of dynamic routing protocol used by routers to exchange routing information within a network.
- It operates based on the principle of "distance" and "vectors" to determine the best path to reach destination networks.
Characteristics of Distance Vector Routing Protocols
- Routing Table Exchange: Routers using distance-vector protocols exchange routing information with neighboring routers.
- Each router maintains a routing table containing information about known destinations and their associated distances.
- Periodic Updates: Routers periodically broadcast routing updates to
- neighboring routers to inform them of any changes in network topology or routing information.
- These updates include the router's known destinations and their associated distances.
- Split Horizon and Poison Reverse: Distance-vector protocols implement mechanisms like split horizon and poison reverse to prevent routing loops and ensure loop-free routing.
Examples of Distance Vector Routing Protocols
Routing Information Protocol (RIP) and Interior Gateway Routing Protocol (IGRP)
Link State Routing Protocols
- Link-state routing protocols are a type of dynamic routing protocol used in computer networks to determine the best paths to reach destination networks.
- link-state routing protocols are dynamic routing protocols that use detailed
- knowledge of the network's topology to calculate the best paths to destination networks.
- link-state protocols are well-suited for large and complex networks where efficient routing and fast convergence are critical.:
Examples of Link-State Routing Protocols
- Open Shortest Path First (OSPF): A widely used link-state routing protocol in IP networks.
- Intermediate System to Intermediate System (IS-IS): Another link-state routing protocol commonly used in large networks,
Exterior Gateway Routing Protocols
- Exterior Gateway Protocols (EGPs) are a category of dynamic routing
- protocols used to exchange routing information between different autonomous systems (ASes) on the Internet or large-scale networks.
- Unlike Interior Gateway Protocols (IGPs), which manage routing within a
- single AS, EGPs facilitate routing between ASes and are responsible for inter-domain routing.
- BGP (Border Gateway Protocol (BGP) is the primary EGP used for this purpose,
- providing scalability, flexibility and robustness in facilitating global connectivity.
Path Vector Routing Protocol
- Path vector routing protocols are key components of inter-domain routing on the Internet, with BGP being the most prominent example.
- These protocols provide policy-based routing and flexible route selection capabilities,
- but they also come with challenges such as complexity, slow convergence, and resource consumption.
- Path vector routing protocols are a type of exterior gateway routing protocol used for inter-domain routing.
Conclusion
Now we have detailed understanding of Static, Dynamic Path Vector ,Routing Protocols , Interior Gateway Routing Protocols (IGPs) , Distance Vector Routing Protocols,Border Gateway Protocol (BGP)