Requirement Analysis | Software Engineering
What is Software Requirement Analysis?
- Software Requirement Analysis in Software Engineering is a critical phase in the software development process.
- Software Requirement Analysis is an in-depth examination of project requirements to understand and analyze what a software system needs to achieve.
Activities Involved in Software Requirement Analysis
- Understanding Stakeholder Needs: Requirement analysts work closely with stakeholders, such as clients to comprehend their needs.
- Requirements Elicitation: Requirement Analysis often begins with Requirement Elicitation, where various techniques, like interviews, and FAST are used to collect information about the project's functional and non-functional requirements.
- Documentation: Analysts document the gathered requirements in a clear and organized manner.
- Validation and Verification: Validation involves confirming that the requirements accurate while verification ensures that they are consistent and meet quality standards.
Software Requirement Analysis Using Diagrams
- DFD (Data Flow Diagrams)
- Use-Case Diagrams
- Sequence Diagrams
- Class Diagrams
- ERD (Entity-Relationship Diagrams)
DFD (Data Flow Diagrams)
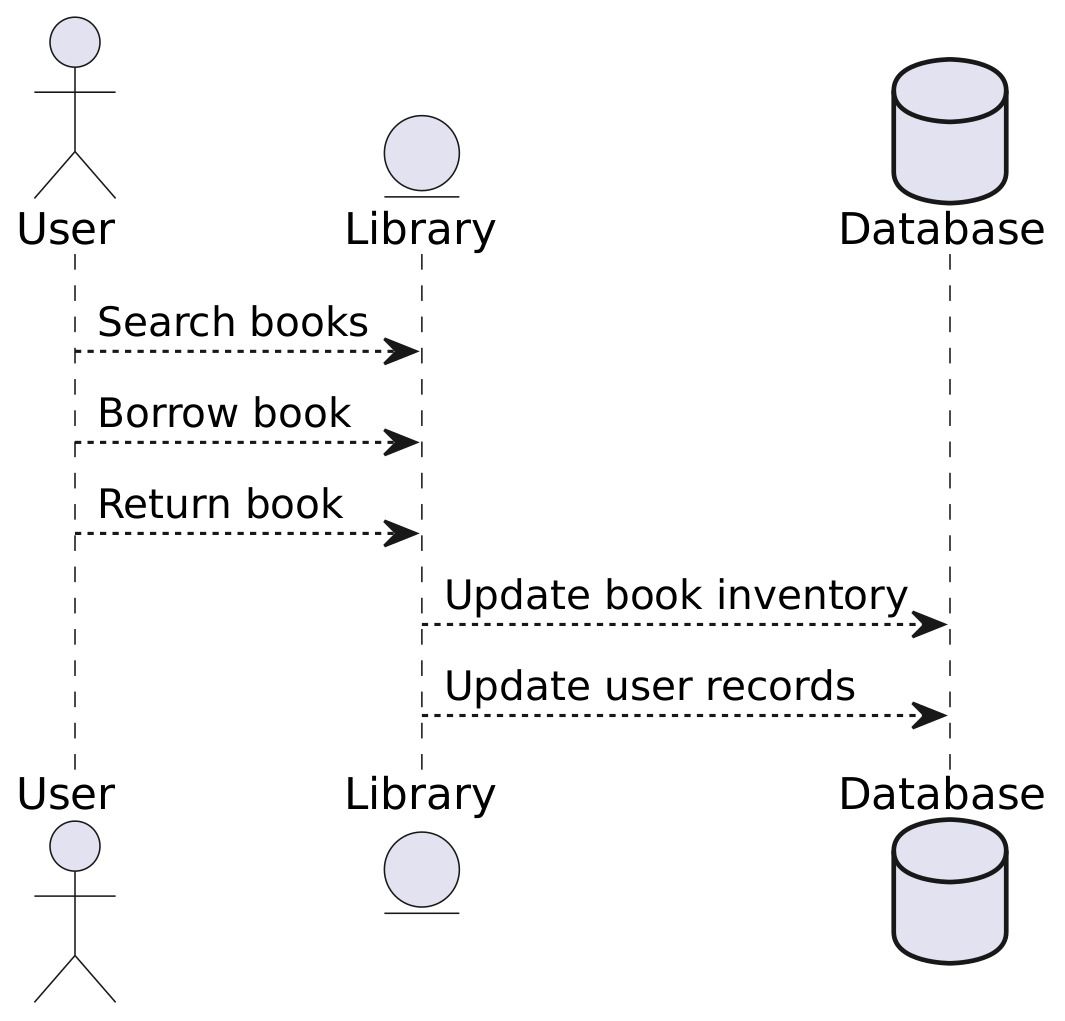
- Data Flow Diagrams (DFDs) are graphical representations that showcase the flow of data within a system.
- In a DFD, there are four main components: processes, data stores, data flows, and external entities.
- For example, let's consider a simple library management system.
- In this case, the external entities would be users (students and librarians), and the processes would include tasks like borrowing books, returning books, and searching for books.
- Data flows represent the information exchanged between these entities and processes, such as user details, and book information.
- Data stores would represent the database where all the book-related information is stored.
Use-Case Diagrams
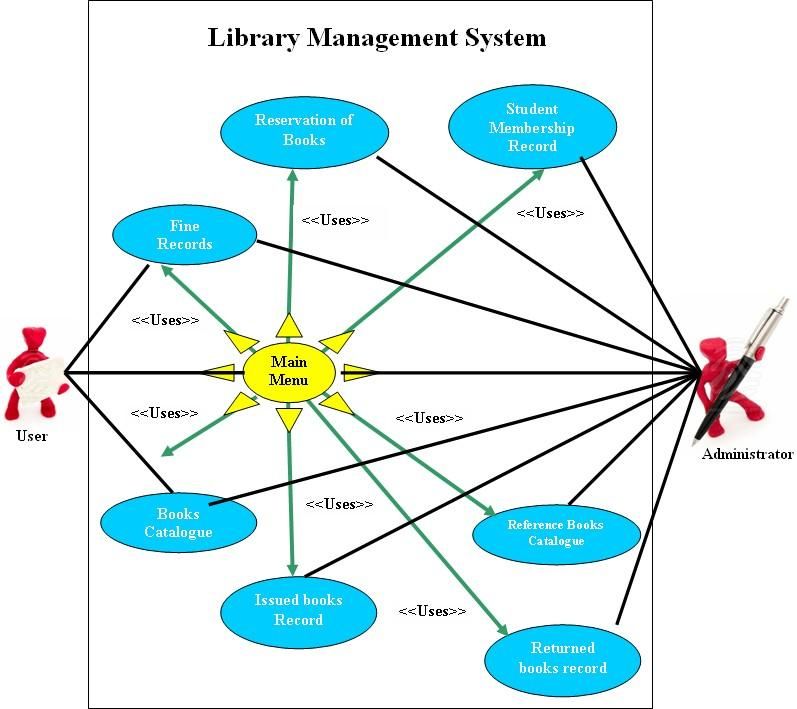
- Use-case diagrams provide a high-level view of the interactions between the system and its actors (users or other systems).
- These diagrams help in identifying the functionalities that the system should provide to its users.
- Continuing with the library management system example, the actors would be students and librarians.
- The use cases would be borrowing books and returning books. These use cases demonstrate the various functionalities required from the system's perspective.
Sequence Diagrams
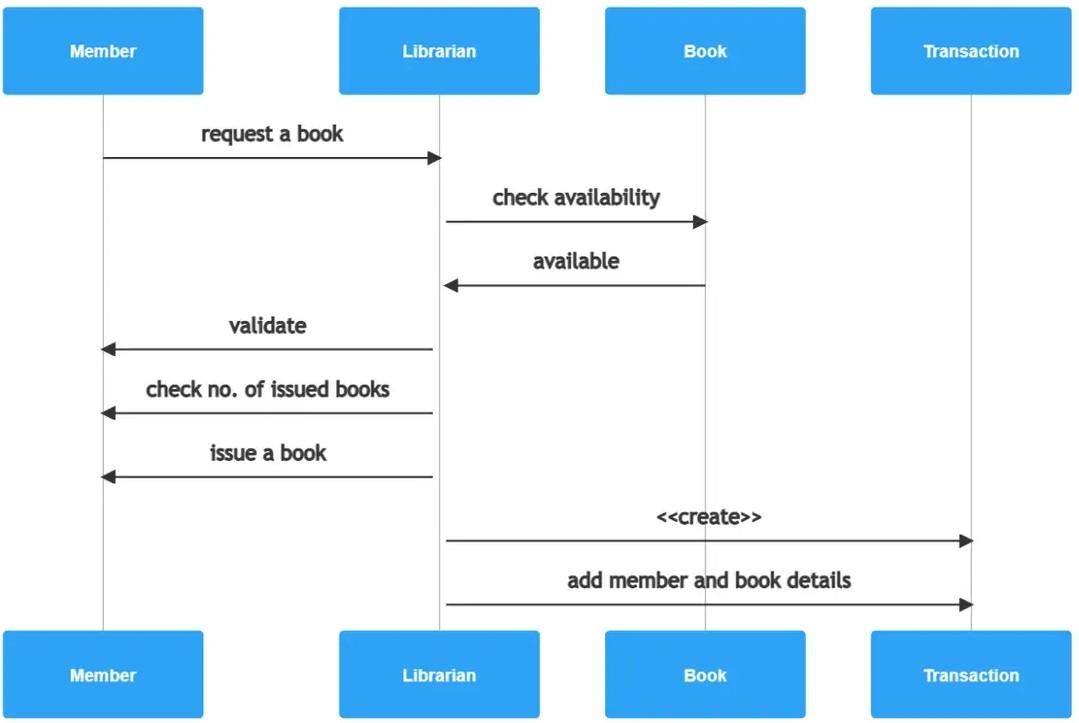
- Sequence diagrams illustrate the flow of interactions between different components or objects within the system over a specific time period.
- They demonstrate how objects collaborate to accomplish a particular task.
- For instance, consider the scenario of a user borrowing a book from the library management system.
- The sequence diagram would show the steps involved, like the user logging in, searching for a book, selecting it, and then successfully borrowing it.
Class Diagrams
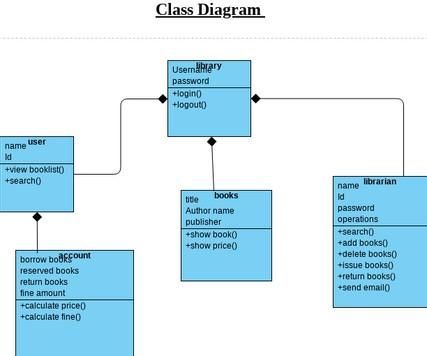
- Class diagrams represent the static structure of the system, showcasing the classes, attributes, and methods involved.
- A class is a blueprint for creating objects with similar characteristics.
- Attributes are the properties of the class, and methods are the actions it can perform.
- Let's continue with the library management system example.
- We would identify classes like Book, User, Library, and Transaction.
- Attributes for the Book class could be title, author, and ISBN.
- For the User class, attributes might include name, address, and contact information.
- Methods would define actions such as searching for a book and returning a book.
ERD (Entity-Relationship Diagrams)
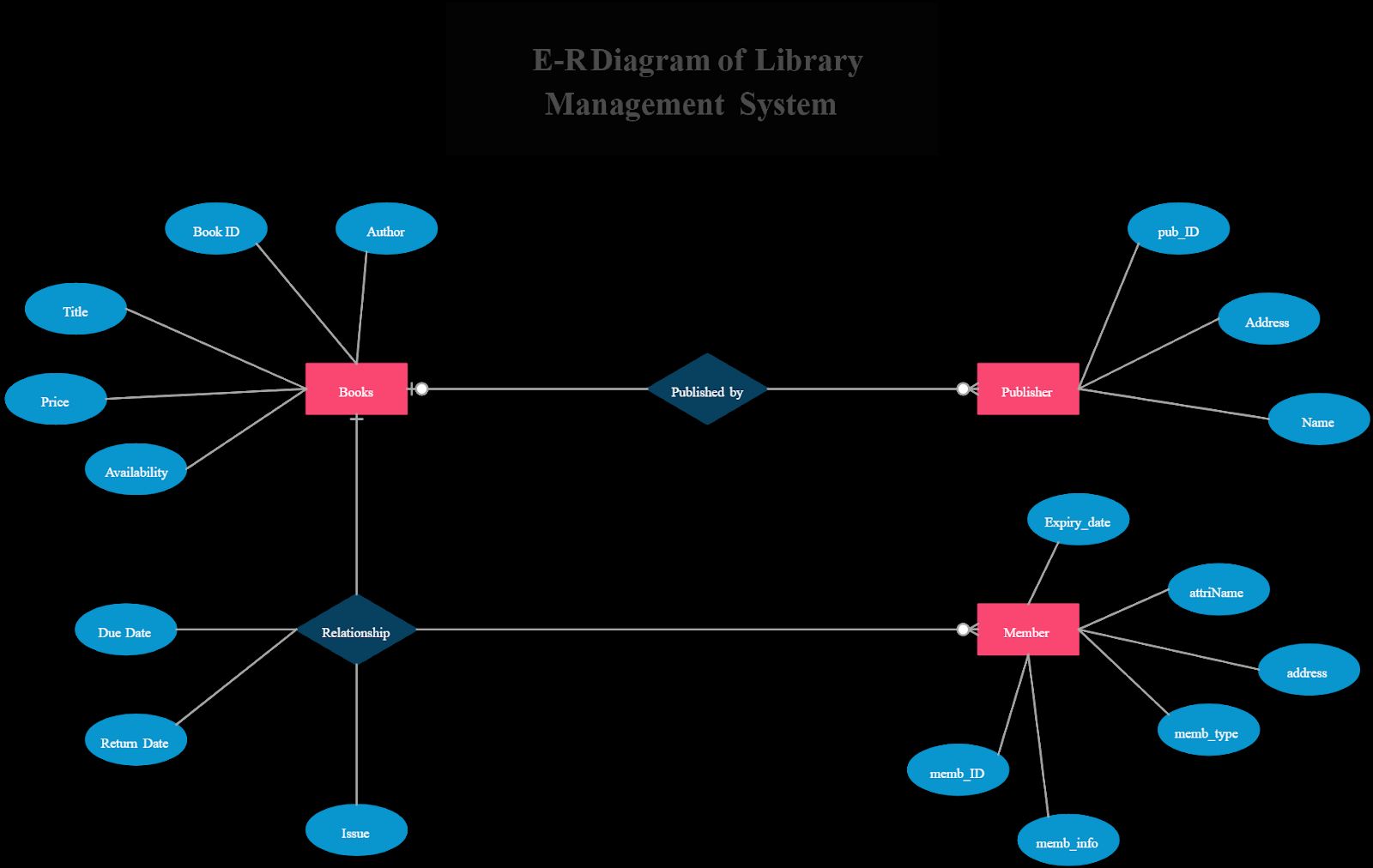
- ERDs (Entity-relationship diagrams) are used to model the database of a software system.
- They illustrate the relationships between entities and their attributes.
- For the library management system, entities would include Book, User, and Transaction.
- The relationships between these entities would be represented, such as "User borrows Book" and "Transaction associates User and Book."
- Attributes for each entity would also be listed, like "BookID," "UserName," etc.
Conclusion
Software Requirement Analysis is a vital phase in software development, involving understanding stakeholder needs and Requirement Elicitation. Software Requirement Analysis often utilizes diagrams like DFDs, Use-Case Diagrams, Sequence Diagrams, Class Diagrams, and ERDs to enhance clarity and communication throughout the process.