
Components, Three tier architecture and Metadata in Dwdm
Components of Data Warehouse
The components of a data warehouse include
Data Sources
- Data sources refer to the various systems, databases, applications,
- and external sources from which data is collected and extracted for storage in the data warehouse.
Types of Data Sources
- Production Data
- Internal Data
- External Data
- Archived Data
Production Data
- Production data refers to the operational data generated by the day-to-day activities of an organization's business processes.
- This includes transactional data, customer interactions, sales records, and other real-time data captured by operational systems.
- Such as (ERP), and customer relationship management (CRM).
Internal Data
- Internal data sources are data generated and collected within the organization's own systems and databases.
- These may include data from internal applications, databases, spreadsheets, files, and other proprietary sources.
External Data
- External data sources are data obtained from sources outside the organization
- such as third-party vendors, partners, suppliers and public sources.
- External data may include demographic data, market trends, etc.
Archived Data
- Archived data refers to historical data that is no longer actively used in production systems
- but is retained for reference, compliance, or analytical purposes.
- This may include historical transaction data, customer records, financial statements,
- and other archived data that is stored in data warehouses .
Data Staging
The data staging process involves three main components: data extraction, data transformation, and data loading. Let's explore each component:
Data Extraction
- Data extraction is the first step in the data staging process.
- It involves retrieving data from various source systems, databases, applications, or external sources.
- The data extraction process can be performed using different methods
- such as database queries, file transfers, APIs (Application Programming Interfaces), or Change Data Capture (CDC) mechanisms.
- The goal of data extraction is to gather relevant data from the source systems and prepare it for further processing.
Data Transformation
- Data transformation is the second step in the data staging process,
- where the extracted data is processed and prepared for loading into the data warehouse.
- This involves applying various operations to the extracted data to cleanse, standardize, enrich, and integrate it with existing data.
- Common data transformation tasks include:
- Cleaning: Removing duplicates, correcting errors, and standardizing formats to ensure data consistency and accuracy.
- Formatting: Converting data types, standardizing date formats, and applying data validations to meet the requirements of the data warehouse.
- Enriching: Enhancing the extracted data with additional attributes, calculations to enrich its value for analysis.
- Aggregating: Summarizing or aggregating data at different levels of granularity or unfiltered to facilitate analysis and reporting.
- The transformed data is typically stored in an intermediate staging area or temporary storage before being loaded into the data warehouse.
Data Loading
- Data loading is the final step in the data staging process,
- where the transformed data is loaded into the data warehouse for storage and analysis.
- This involves inserting, updating, or appending the transformed data into the appropriate tables within the data warehouse.
- Data loading can be performed using different loading techniques such as
- bulk loading, incremental loading, or real-time loading, depending on the volume and frequency of data updates.
- The loaded data is stored in the data warehouse in a structured format,
- ready to be queried, analyzed by users or business intelligence tools.
Data Storage Component
- Data storage encompasses or bound the infrastructure and
- processes involved in securely storing the transformed and integrated data collected from various sources.
- This component utilizes a relational database management system (RDBMS) to organize and
- manage structured data based on a predefined schema, which can be either dimensional or normalized.
- The data is structured into tables, rows, and columns to facilitate efficient querying, analysis, and reporting.
- Data storage also manages data retention, ensuring that historical data is retained for analysis.
Information Delivery Component
- The Information Delivery component encompasses or surround tools and
- processes that enable users to access, analyze, and derive insights from the data stored in the warehouse.
- This includes query and reporting tools for retrieving specific information and generating reports,
- OLAP tools for multidimensional analysis, data visualization tools for creating visual representations of data.
Three Tier Architecture
- The three-tier architecture refers to a design framework that organizes the components of a data warehouse into
- three distinct layers: the presentation layer, the application layer, and the data layer.
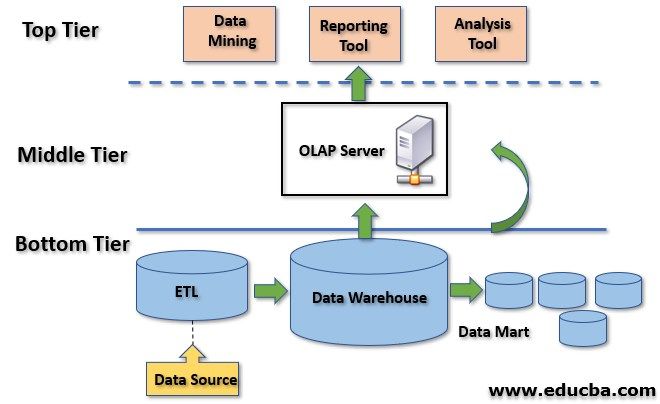
Presentation Layer (Front-end Layer)
User Interfaces
- The presentation layer includes user interfaces such as web-based dashboards, reporting tools,
- and interactive visualization applications that allow users to access and interact with the data stored in the warehouse.
Data Visualization
- It provides tools and capabilities for visualizing data through charts, graphs, heatmaps,
- and other graphical representations, making it easier for users to understand and interpret complex data sets.
Customization Options
- Users can customize the presentation layer according to their preferences, such as selecting specific metrics,
- adjusting visualization settings, and creating personalized dashboards tailored to their analytical needs.
Interactivity
- The presentation layer enables users to interact with the data dynamically, such as filtering data,
- drilling down into details, and exploring different dimensions, to gain deeper insights and make informed decisions.
Accessibility
- It ensures that data is presented in a user-friendly and accessible manner, with intuitive navigation,
- responsive design, and support for various devices and screen sizes to accommodate diverse user needs.
Application Layer (Middle Tier)
Business Logic
- The application layer encapsulates or summarize the business logic and processing rules that govern how data is accessed,
- manipulated, and managed within the data warehouse environment.
Query Processing
- It handles tasks related to query optimization, execution, and performance
- tuning to ensure that queries are processed efficiently and accurately, delivering timely results to users.
Data Transformation
- The application layer performs data transformation tasks, such as cleansing, standardization,
- to prepare data for analysis and reporting in the presentation layer.
Security Enforcement
- It enforces security policies and access controls to ensure that only authorized
- users can access and modify data, protecting sensitive information and maintaining data privacy and confidentiality.
Integration Services
- The application layer facilitates data integration by integrating data from multiple source systems,
- arrange data flows, and ensuring data consistency and reliability across the data warehouse environment.
Data Layer (Back-end Layer or Storage Layer)
Data Storage
- The data layer stores the cleansed, and transformed data from various source systems in a structured format within the data warehouse,
- typically using a relational database management system (RDBMS) or data storage technology.
Data Management
- It manages data storage, retrieval and organization to ensure data integrity,
- and accessibility for querying, analysis, and reporting purposes.
Scalability
- The data layer is designed to scale horizontally or vertically to accommodate growing data volumes and
- evolving analytical needs, ensuring that the data warehouse can handle increasing data loads and user demands.
Data Governance
- It implements data governance policies and practices to govern data quality,
- metadata management, data lineage, and compliance with regulatory requirements and organizational standards.
Performance Optimization
- The data layer optimizes database performance through techniques such as
- indexing, partitioning, caching, and compression to enhance query speed, reduce latency, and improve overall system performance.
Meta Data
- Metadata in a data warehouse refers to data about the data stored within the warehouse.
- It provides essential information about the structure, content, and context of the data, facilitating
- understanding, management, and utilization of the data within the warehouse environment.
- Metadata includes details such as data definitions, data lineage, data sources, transformations, and business rules.
- It helps users interpret and utilize the data effectively, ensuring data quality,
- uniformity, and adherence to organizational standards and regulations.
Conclusion
We have explored Components such as Data sources, Data Staging , data loading , three tier architecture such as Data, Application layer and Metadata in the data warehouse.